Active Directory How-To
Breaking Down Server Roles in Active Directory
Here's how to apply a server role, along with a brief description of the multiple roles that can be chosen.
- By Troy Thompson
- 12/10/2015
In this article, we will look at the different roles available to install on a server in an Active Directory environment. To install the different roles on a Windows Server, you will user the Server Manager utility. Server Manager can be accessed through Control Panel and replaces the Add or Remove Windows Components. It is a single tool that allows the following:
- View and make changes to server roles and features installed on the server.
- Perform management tasks associated with the operational life cycle of the server, such as starting or stopping services, and managing local user accounts.
- Perform management tasks associated with the operational life cycle of roles installed on the server. This includes scanning roles for compliance with best practices.
- Determine server status, identify critical events, and analyze and troubleshoot configuration issues or failures.
The Add Roles Wizard
The Add Roles Wizard simplifies how you install roles on the server, and lets you install multiple roles at one time. The Wizard verifies that all the software components that are required by a role install with any role that you select. If a role has a prerequisite, you will be prompted to approve the installation of other roles, role services, or software components. Once Server Manager is open, right-click the Roles icon to access the menu as shown in Figure 1.
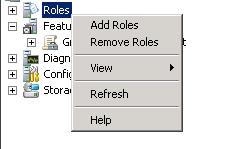 Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Adding Roles and Features to a Server
Roles or features can be added to a server by using one of the following three procedures:
- Windows Interface
- Windows PowerShell
- Command Line
For the purposes of this article, we will only look at adding server roles using the Windows Interface.
Figure 2 shows the Add Roles Wizard and the different roles that can be installed. Roles that are already installed will appear with a checkmark and will be greyed out.
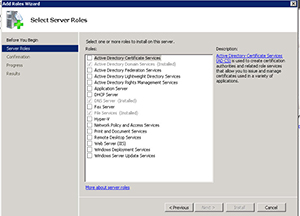 [Click on image for larger view.] Figure 2.
[Click on image for larger view.] Figure 2.
Active Directory Certificate Services
Active Directory Certificate Services Active Directory Certificate Services provides customizable services for issuing and managing certificates in software security systems that use public key technologies. You can use it to create one or more certification authorities (CA) to receive certificate requests, verify the information in the requests and the identity of the requester, issue certificates, revoke certificates, and publish certificate revocation data.
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Domain Services stores information about users, computers, and other devices on the network. It helps administrators securely manage this information and facilitates resource sharing and collaboration between users. You must have it installed on the network in order to install directory-enabled applications such as Microsoft Exchange Server and for applying other Windows Server technologies such as Group Policy.
Active Directory Federation Services
Active Directory Federation Services provides Web single sign-on (SSO) technologies to authenticate a user to multiple Web applications that use a single user account.
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services runs as a non-operating-system service and does not require deployment on a domain controller. Running as a non-operating-system service allows multiple instances to run at the same time on a single server.
Active Directory Rights Management Services
Active Directory Rights Management Services is information protection technology that works with AD RMS -enabled applications to help safeguard digital information from unauthorized use.
Application Server
An Application Server provides a complete solution for hosting and managing high-performance distributed applications.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows servers to assign, or lease, IP addresses to computers and other devices that are enabled as DHCP clients. A DHCP server can automatically provide computers and other TCP/IP based network devices with valid IP addresses as well as additional configuration parameters such as DNS servers, WINS servers, and routers.
DNS Server
Domain Name System (DNS) associates domain names with Internet addresses. This helps users by letting them refer to network computers by name instead of IP addresses.
Fax Server
Fax Server sends and receives faxes, and lets you manage fax resources such as jobs, settings, reports and fax devices on this computer or on the network.
File Services
File Services provides for storage management, file replication, distributed namespace management, fast file searching and streamlined client access to files.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V allows you to create and manage virtual computing environments and their resources. With a virtual computer, you can run multiple operating systems at the same time.
Network Policy and Access Services
Network Access Services allows you to deploy VPN servers, dial-up servers, routers, and 802.11-protected wireless access. You can also use it to deploy RADIUS servers and proxies.
Print and Document Services
Print and Document Services allows you to centralize print server and network printer management tasks.
Remote Desktop Services
Remote Desktop Services provides users access to Windows-based programs that are installed on a remote desktop server or to access the desktop itself.
Web Server (IIS)
The Web Server (IIS) lets you share information with users on the Internet, an intranet, or an extranet.
Windows Deployment Services
Windows Deployment Services is used to install and configure remote Windows operating systems on computers that have Pre-boot Execution Environment (PXE) enabled.
Windows Server Update Services
With the Windows Server Update Services installed, network administrators can specify the Microsoft updates that should be installed on Windows clients.
Server Manager cannot be used to manage a newer release of the Windows Server operating system. For instance, Server Manager running on Windows Server 2012 or Windows 8 cannot be used to install roles, role services, and features on servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2. To remove roles and features in Server Manager, choose Remove Roles and Features from the Manage menu.
About the Author
Troy Thompson has worked in network administration for over 25 years, serving as a network engineer and Microsoft Exchange administration in Department of Defense, writing technology articles, tutorials, and white papers and technical edits. Troy is a Cisco Certified Academy Instructor (CCAI), and has numerous other certifications including CCNA, MSCE+I, Network+, A+ and Security+. Troy has also traveled the world playing music as the guitarist for the band Bride. Contact information is [email protected].